Abstract
BACKGROUND: GRFS is a composite endpoint developed by the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) to reflect the major outcomes post HCT. Events in GRFS include grade 3-4 acute GVHD (aGVHD 3-4), systemic therapy-requiring chronic GVHD (cGVHD), relapse, or death. We reported that bone marrow (BM) grafts from matched sibling donor (MSD) led to best GRFS at 1-and 2-years compared with peripheral blood (PB) grafts from any donor or umbilical cord blood (UCB). (Holtan et. al. Blood 2015 & Mehta et.al. Haematologica. 2016) These studies excluded haploidentical (haplo) and mismatched (MM)-HCT. The outcomes of this composite endpoint in alternative donor HCT is unknown. Here, we analyzed GRFS and chronic GVHD-free relapse-free survival (CRFS) among alternative donor HCT (UCBT, haplo, one-antigen MM (7/8)-BM or 7/8-PB HCT) for patients with no MSD or matched unrelated donor.
METHODS: Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission, chronic myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome who received alternative donor HCT from 2000-2014 were included. Only those haplo patients who received post-HCT cyclophosphamide and only those UCBT done using fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation myeloablative (MA) or reduced intensity (RIC) with or without antithymocyte globulin (ATG) were analyzed. Exclusion criteria were prior autologous or allogeneic HCT, ex-vivo T-cell depletion or CD34 selection and those with UCB unit <4/6 HLA match. Multivariable analysis was done using Cox's proportional hazards (PH) modeling with time-dependent adjustments as needed for stepwise modeling, selecting factors using a threshold of 0.05 for both entry and retention in the model. CRFS was defined survival without cGVHD or relapse.
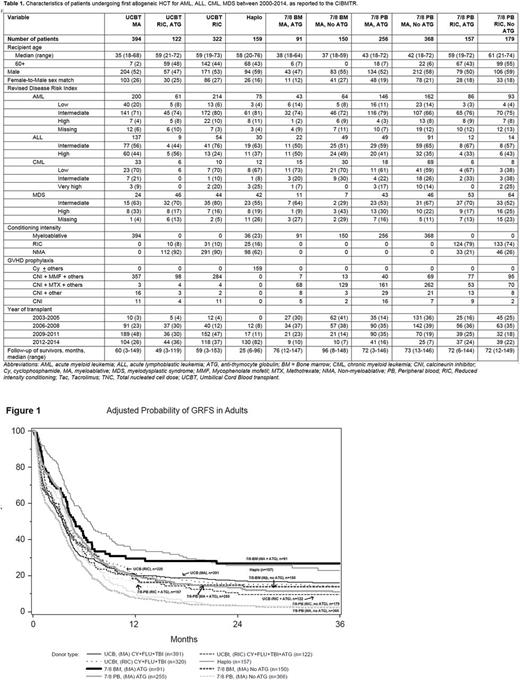
RESULTS: 2198 patients were analyzed, including UCBT (n=838), haplo (n=159), 7/8-BM (n=241) and 7/8-PB (n=960). Groups (except haplo) were further divided by conditioning and ATG use [Table 1]. AML was most common diagnosis (52%). As expected, patients who received MA conditioning were younger (median 35-43 years) than those who got RIC (median 58-61 years). 81% of UCB group received double cord. Most patients in haplo group received BM graft (71%), and a majority (82%) were from 2012-2014; consequently, follow-up of haplo group (median 25 months) was shorter than others (49-96 months).
In multivariate analysis of early post-HCT outcomes (within 4.5 months) adjusted for year of HCT and other covariates, as compared to haplo, UCB, 7/8-BM (MA, no ATG) and 7/8-PB had inferior GRFS. However, beyond 4.5 months, haplo, UCB and 7/8-BM (MA +/- ATG) had similar GRFS while 7/8-PB had inferior GRFS. [Fig 1] Likewise, beyond 4.5 months, as compared to haplo, CRFS was similar in UCB and 7/8-BM (MA +/-ATG), while 7/8-PB had inferior CRFS.
As compared to Haplo, risk of aGVHD was significantly higher in all groups, except UCB (RIC + ATG) and the risk of cGVHD (beyond 4.5 months) was higher in 7/8-BM (MA, no ATG) and 7/8-PB but similar in UCB and 7/8-BM (MA + ATG). As compared to haplo, risk of relapse was significantly lower after UCB (MA), 7/8-BM (MA +ATG) and 7/8-PB (MA, no ATG), similar in UCB (RIC + ATG), 7/8-BM (MA, no ATG), 7/8-PB (MA + ATG) and 7/8-PB (RIC +/-ATG) and higher in UCB (RIC, no ATG). Haplo had superior disease free survival compared to UCB, 7/8-PB (MA, no ATG) and 7/8-PB (RIC + ATG), but it was similar in 7/8-PB (MA + ATG) and 7/8-BM (MA +/-ATG). Similarly, haplo had superior overall survival compared to any other group.
CONCLUSION: Long-term morbidity and mortality as measured by GRFS and CRFS are similar in UCBT, haplo and 7/8 BM groups. The use of 7/8-PB should be avoided given substantially poor GRFS and CRFS. As 7/8-BM group included only younger patients who received MA conditioning, no conclusion can be drawn about its outcome in older patients, for whom either haplo or UCB remain as the preferred donor source. These outcomes may also be a reflection of different GVHD prophylaxis regimens rather than donor type. Ongoing randomized comparison of UCBT versus haplo in the BMT CTN 1101 trial will prospectively evaluate these two groups.
Holtan: Incyte: Other: One-time advisory board member. Arora: Takeda Oncology: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal